Sin Cos Tan Csc Sec Cot Chart
The formula of Trigonometry : Trigonometry is a well-acknowledged name in the geometric domain of mathematics, which is in relevant in this domain for ages and is also practically applied across several occasions.
- Integration Formula
- Trig Identities
- Formula of Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometric functions with Formulas
- What are Trigonometric derivatives
- Heights and distance
- Trigonometry formula Involving Sum Difference Product Identities
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Differentiation Formula
- Basic Trig Identities
In simple language, trigonometry can be defined as that branch of algebra, which is concerned with the triangle. In this branch, we study the relationship between angles and the side length of a given triangle. With this detailed study of triangles, several types of equations are formed, which are consequently solved to simplify the relationship between the side and angle lengths of such triangles.
Trigonometry is considered one of the oldest components of Algebra, which has been existing around since the 3rd century. There are practical usages of trigonometry in several contexts such as in the domain of astronomy, surveying, optics, or periodic functions.
Formula of Trigonometry
Well, whether it is algebra or geometry both of these mathematics branches are based on scientific calculations of equations and we have to learn the different formulas to have easy calculations.
As we know that in Trigonometry we measure the different sides of a triangle, by which several equations are formed. Further, the formulas of Trigonometry are drafted following the various ratios used in the domain, such as sine, tangent, cosine, etc. So, there are the numbers of the formulas which are generally used in Trigonometry to measure the sides of the triangle.
Here below we are mentioning the list of different types of formulas for Trigonometry.
-
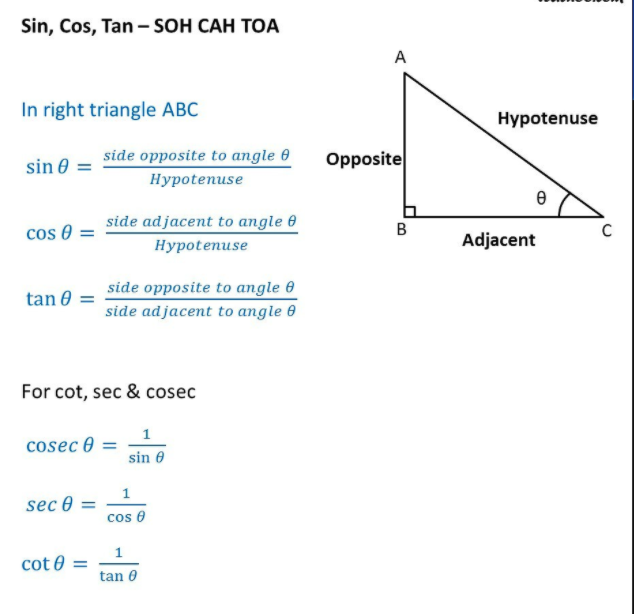
Trigonometry Basic Formula
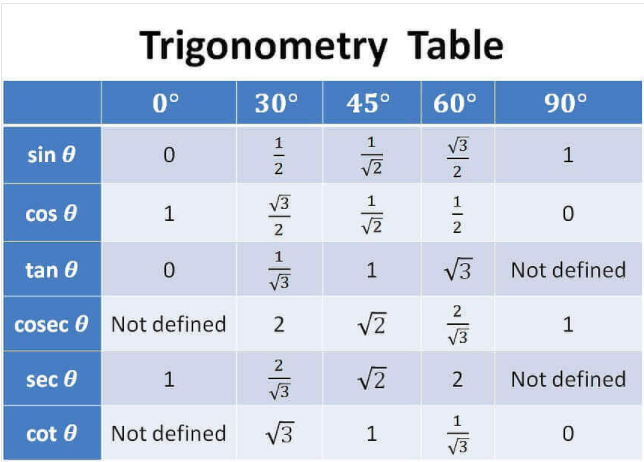
2. Sin Cos Tan at 0, 30, 45, 60 Degree
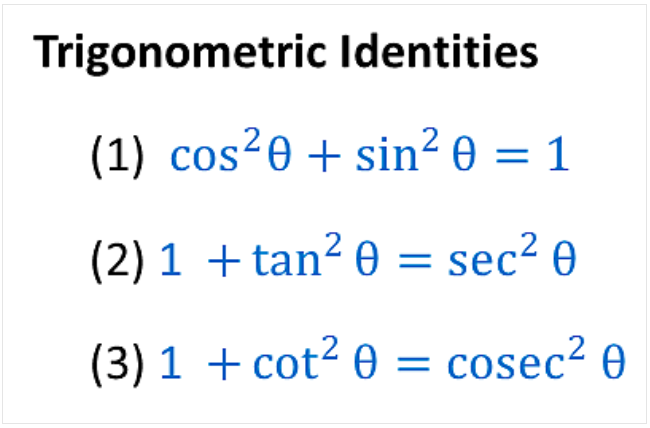
3. Pythagorean Identities
4. Sign of Sin, Cos, Tan in Different Quadrants
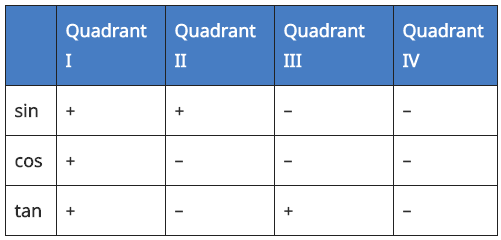
A dd– Sugar–To –Coffee
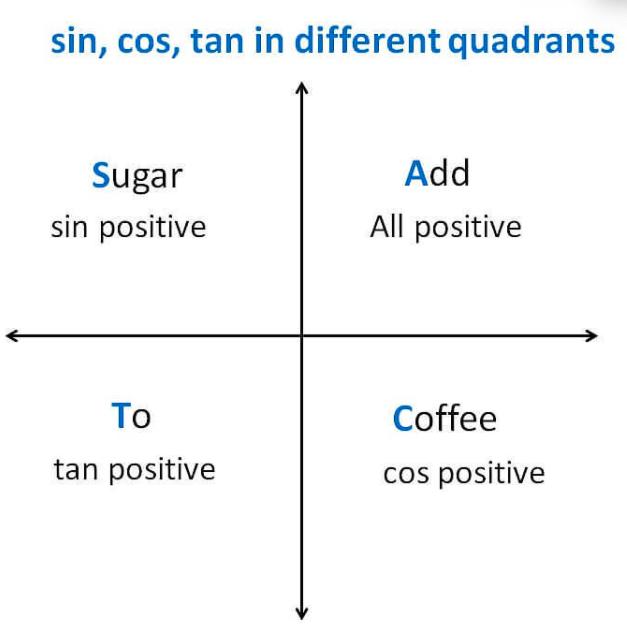
5. Radians
![]()
1 Degree = 60 Minutes
Ex:1 °= 60′
1 Minute = 60 Seconds
Ex:1′ = 60"
6. Negative Angles [Even-Odd Identies]
Sin (-x) = – Sin x
Cos (-x) = Cos x
Tan (-x) = – Tan x
Cot (-x) = – Cot x
Sec (-x) = Sec x
Cosec (-x) = – Cosec x
7. Value of Sin, Cos, Tan repeat after 2𝛑
Sin (2𝛑 + x) = Sin x
Cos (2𝛑 + x) = Cos x
Tan (2𝛑 + x) = Tan x
8. Periodicity Identities – Shifting Angles by 𝛑/2, 𝛑, 3𝛑/2
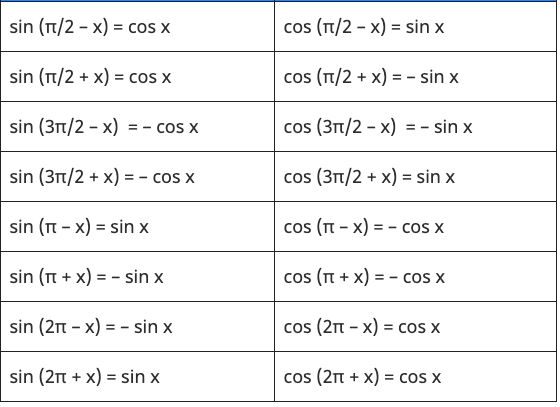
9. Angle Sum & Difference Identities
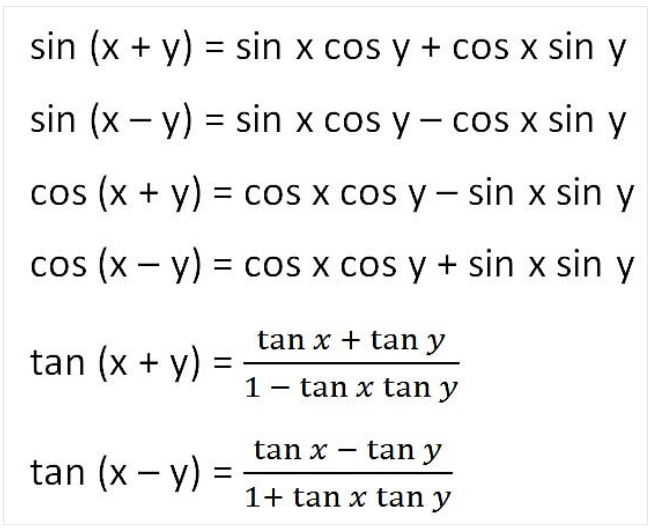
10. Double Angle Formula
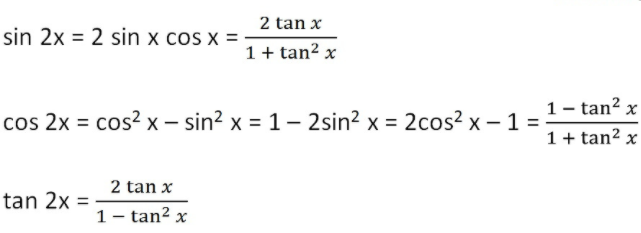
11. Triple Angle Formula
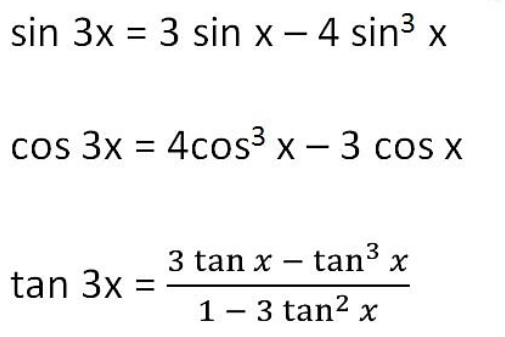
12. Half Angle Identities
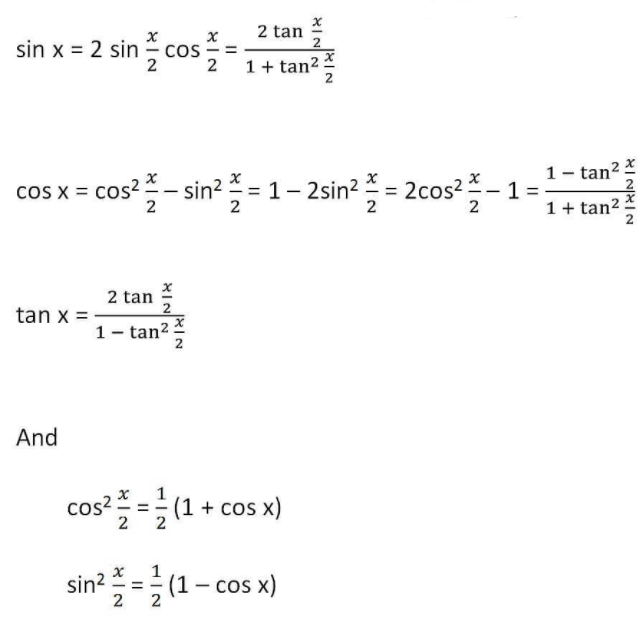
13. Sum Identities
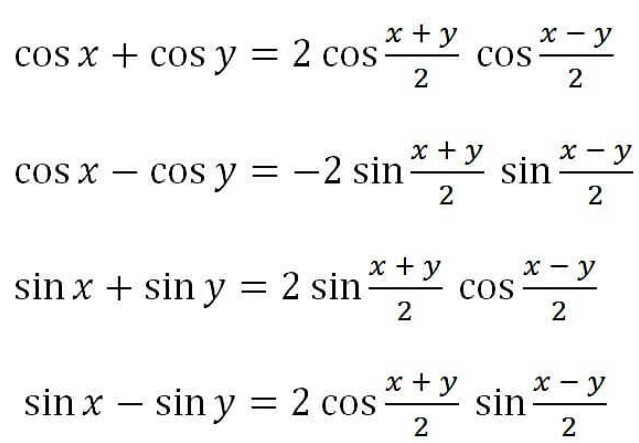
14. Product Identities

15. Law of Sin
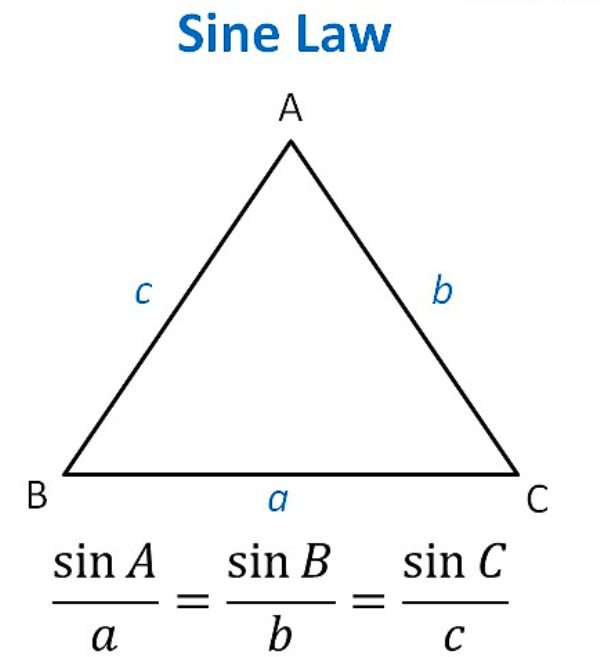
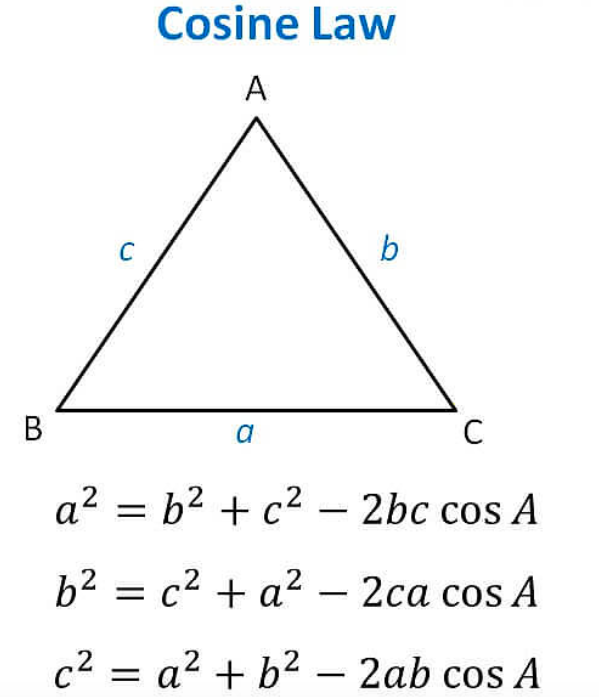
Here,
- ABC are the vertices of the triangle Fonem.
- The opposite site of angle A is a. i.e. BC
- The opposite site of angle B is b. i.e. AC
- The opposite site of angle C is c. i.e. AB
16. Law of Cosine
17. Inverse Trigonometric Function
If Sin θ = x
then Put Sin on the right side
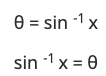
So, By this, you can see that Sin is an angle, Same as Inverse of all Trignomentry function is an angle.
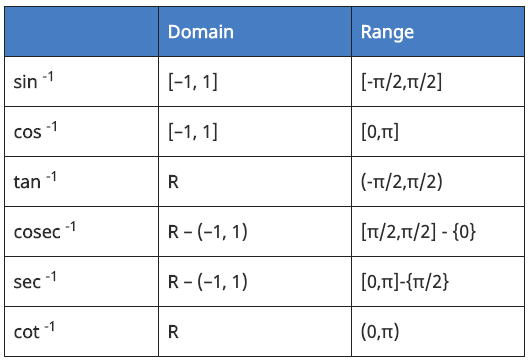
18. Domain and Range of Inverse Trigonometry Functions
19. Inverse Trigonometry Formula
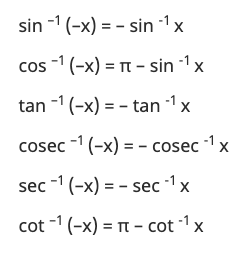
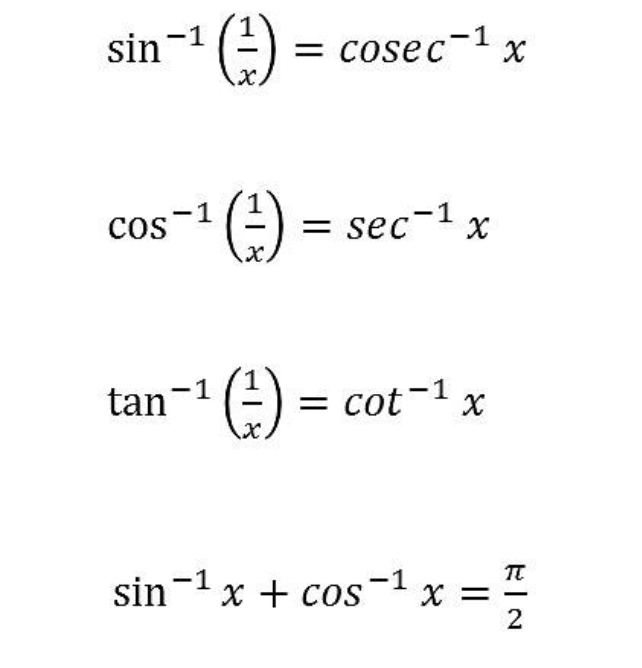
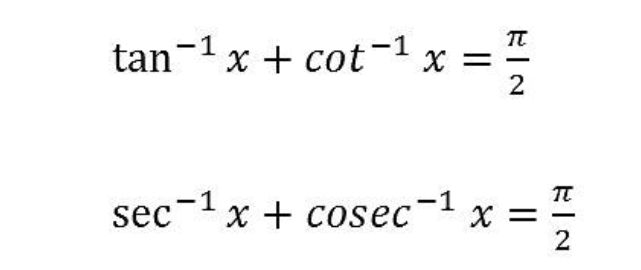
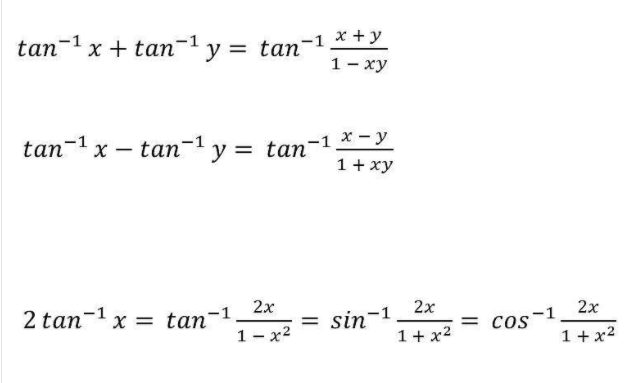
20. Inverse Trigonometry Substitution
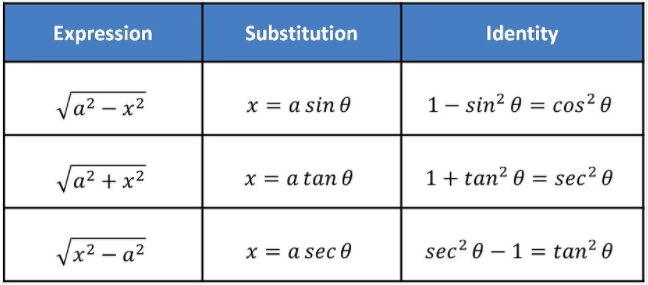
Just like any other branch of mathematics, the formulas of Trigonometry are equally important, since without these formulas you can't put the values of triangles for the measurement purpose. These formulas are what simplifies the sides of triangles so that you can easily measure all their sides.
We urge all scholars to understand these formulas and then easily apply them to solve the various types of Trigonometry problems.
Sin Cos Tan Csc Sec Cot Chart,
Source: https://trigidentities.net/formulas-of-trigonometry/
Posted by: easleyhorabler75.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Sin Cos Tan Csc Sec Cot Chart"
Post a Comment